
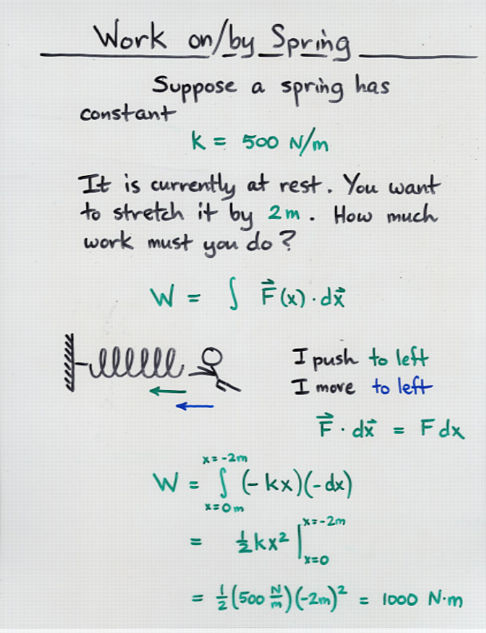
These formulas are very simple but very important for computations. Distance is directly proportionate to Velocity i.e speed of the object when time is constant. Speed is a very common concept in motion which is all about how slow or fast any object travel. This time can be calculated by dividing the distance with speed given. Similarly, we can compute time during the motion to cover some distance with some known speed. Thus distance is the product of speed with time. To find the distance, we need to know the time and speed of the object. To find the speed, we need distance traveled over some known time period. When you are doing work against continuous resistive forces, such as gravity or spring tension, you change the potential energy of the object.2 Solved Examples Time Formula Physics Concept of Speed, Distance and Time When you accelerate the object, you are doing work against inertia, such that the work equals the change in kinetic energy of the object. There is a relationship between that work and mechanical energy. When you apply enough force on an object to overcome a resistive force, such that you move that object, you are doing work on that object. In this situation, the total work done is: If you project an object upward, you are doing work both against gravity and inertia.
Thus in certain situations, work is the change in potential energy. If you lifted the object to another height ( h f), the new potential energy would be: h i is the initial height above the ground.Example with gravityįor example, the PE of an object due to the force of gravity is: Moving the object from one PE to a higher one requires work, which can be measured by the change in potential energy ( ΔPE). This is called its potential energy ( PE). Some resistive forces, such as gravity and spring tension, act continuously on an object, such that the object has a potential of moving from its present position. ( See Proof that Work Can be the Change in Kinetic Energy for more information.) Work as the change on potential energy Thus, in certain situations, work is the change in kinetic energy. v f is the final velocity of the object.Δ means change (Greek letter capital delta).The work done in changing the velocity against some resistance is then equal to the change in kinetic energy of the object: KE is the kinetic energy in J or kg-m 2/s 2.This means that the object's velocity-and thus its kinetic energy-changes over the distance moved.
Work equation physics plus#
When you accelerate an object, you are doing work against inertia plus any resistive forces-such as gravity or friction-over the distance that the object is accelerated. When you accelerate an object, you are changing its velocity. Thus, if you would apply a force of F = 3 newtons (3 N) to overcome inertia and perhaps friction and move an object a distance of d = 5 meters (5 m), the work done would be W = Fd = 15 joules. d is the distance or displacement the object moves in the direction of the force in meters (m).F is the force applied to an object, overcoming any resistance, in newtons (N or kg-m/s²).W is the work in joules (J or kg-m²/s²).Note: Unfortunately, many Physics textbooks carelessly omit the idea that there is the resistive force force of inertia, as well as other possible resistances. The definition of mechanical work (as opposed to thermodynamic work) is that it equals a force against some resistance times the distance traveled while that force is being applied. When is work the change in potential energy?.How is work the change in kinetic energy?.When you are doing work against continuous resistive forces, such as gravity or spring tension, work done equals the change in potential energy of the object. You are doing work against inertia, such that the work equals the change in kinetic energy of the object. Thus, you arwe doing work against inertia By accelerating the object over a period of time, you are moving the object some distance, while changing its veleocity. When you accelerate an object, you are changing its velocity and thus its KE. When you accelerate an object, you are doing work against inertia, such that the work equals the change in kinetic energy of the object.Ĭhange in KE means you have accelerated the object. In certain situations there is a relationship between that work and mechanical energy (as opposed to heat or radiant energy). If there is no distance, there is no work, no matter what the effort. Work is the measurement of the force on an object that overcomes a resistive force (such as friction or gravity) times the distance the object is moved.
Relationship between Work and Mechanical Energy


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
